Best Seller
Elcometer 138/2 Surface Contamination Kit E138—-2
$970.20
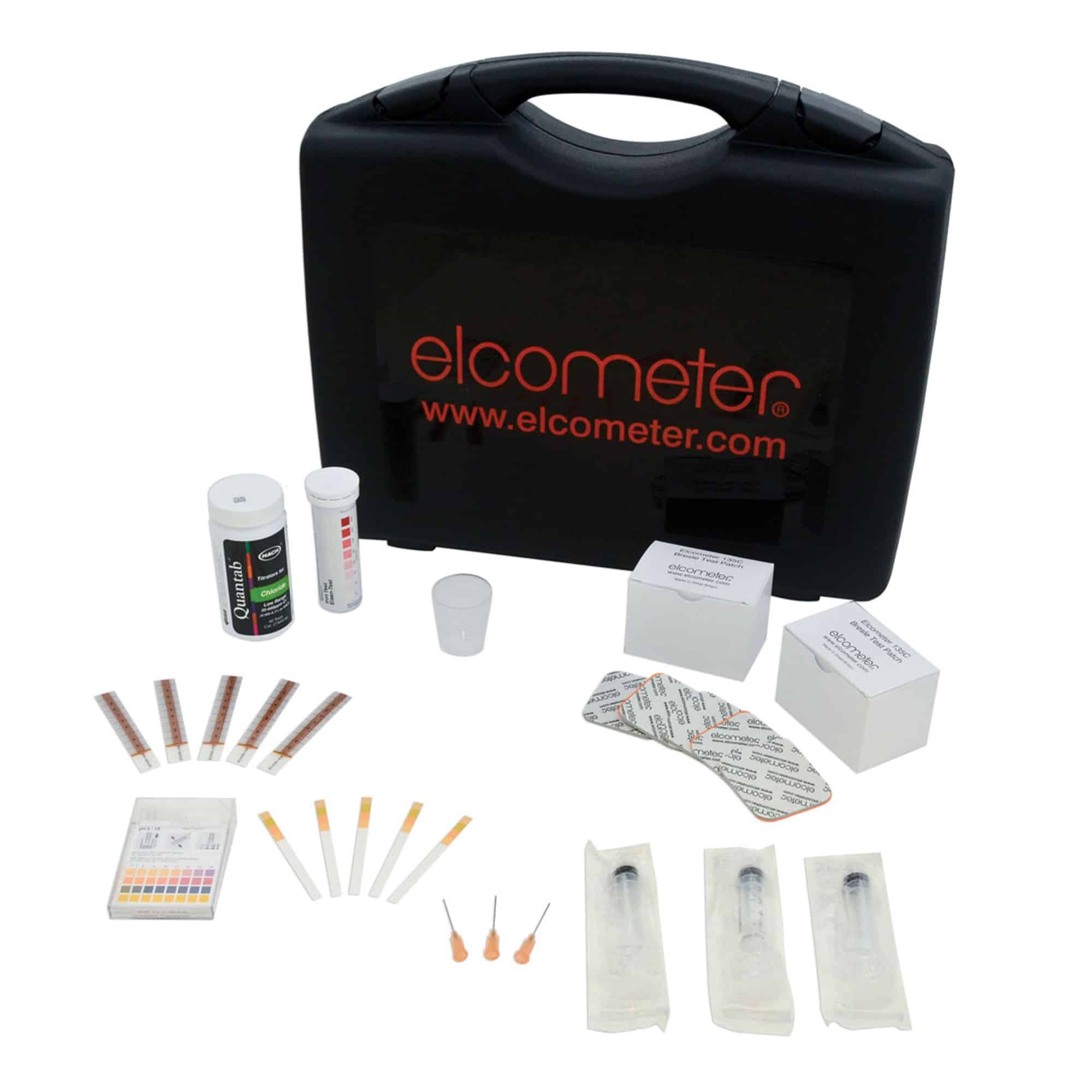
Elcometer 138/2 Surface Contamination Kit
Measuring the level of contaminants on a surface prior to application of the coating is essential to ensure the quality of the coating and that its optimum lifetime is achieved.
If the coating is applied to a contaminated surface, which is not properly prepared, it could fail prematurely resulting in costly recoating and high maintenance costs.
The Elcometer 138/2 Surface Contamination Kit provides the user with a means for testing invisible surface contaminants including:
- pH
- chloride ions
- iron
- salts
In stock